Throughout history, various cultures have harbored beliefs in supernatural entities, with vampires holding a particularly eerie fascination. The recent archaeological discoveries of “vampire burials” have sparked immense curiosity and debate, shedding light on ancient rituals involving the insertion of rocks into the mouth and driving stakes through the chest. These practices, often associated with preventing the deceased from resurrecting as a vampire, unveil intriguing insights into the beliefs and fears of past societies.
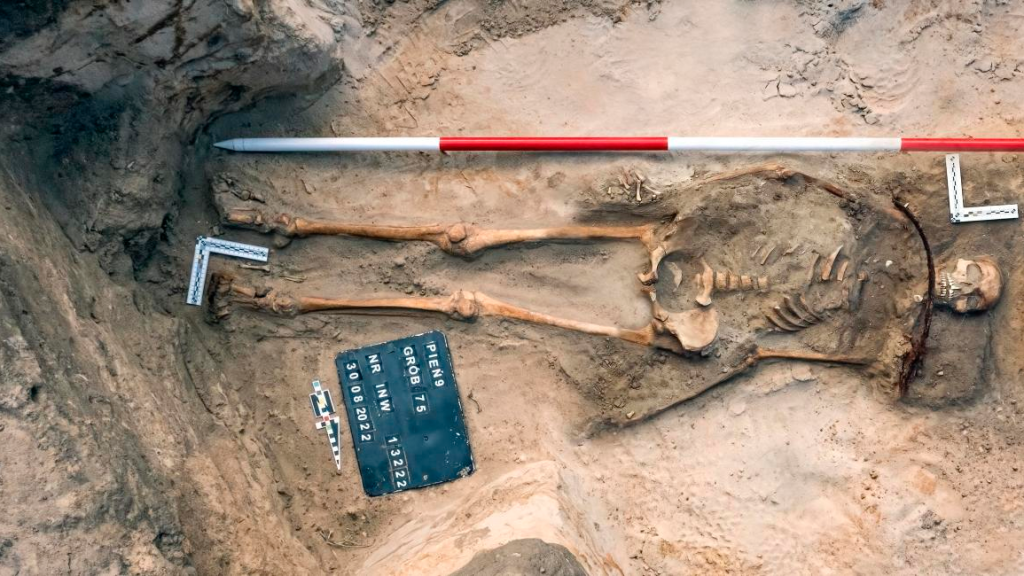

These unconventional burial rituals, discovered in different parts of the world, particularly in Europe, signify a blend of folklore, superstition, and cultural practices. Researchers have unearthed graves dating back centuries where bodies were buried with meticulous precautions against potential revenant activity.
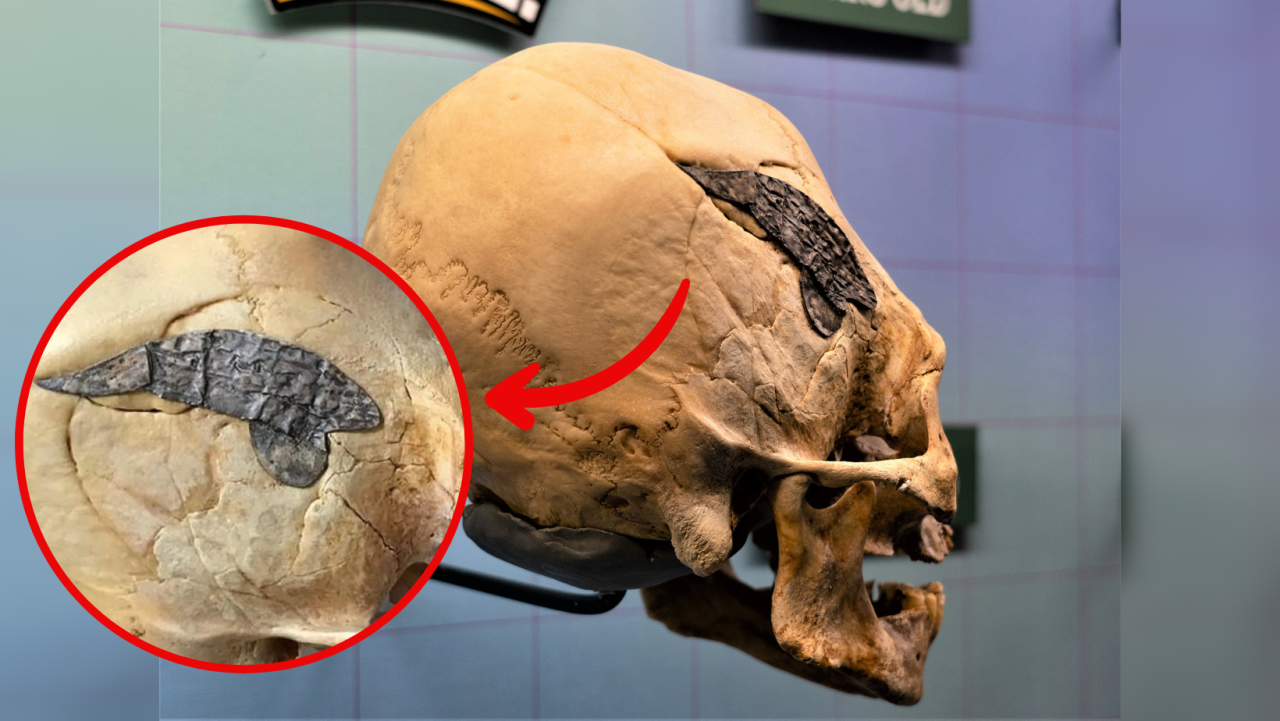
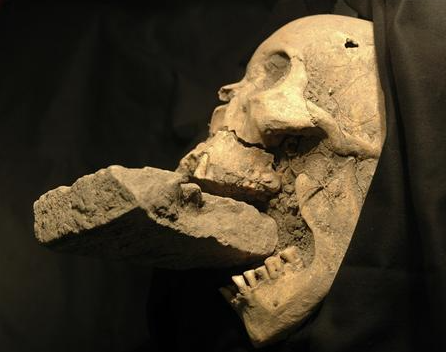
One of the most striking aspects of these burials is the placement of rocks or stones within the deceased’s mouth. This act, presumed to prevent the deceased from rising and feeding on the living, reflects a deep-seated fear of the dead returning to life as malevolent creatures. The belief in the undead and the necessity to restrain their supposed abilities played a crucial role in the implementation of these rituals.
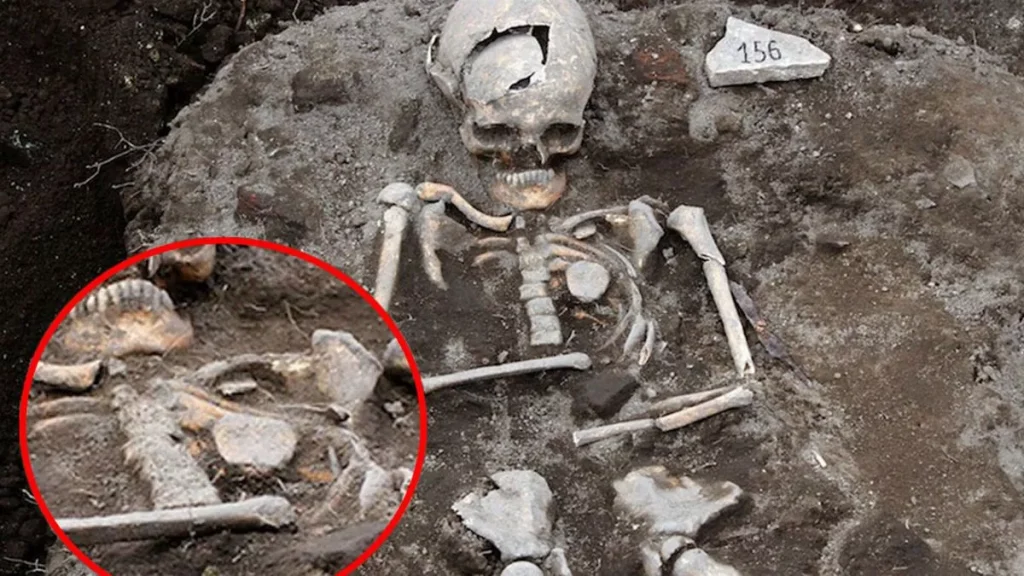
Additionally, the driving of stakes or other objects through the chest or heart area of the deceased aimed to pin the body to the ground, rendering it immobile and incapacitated from haunting the living. This act echoes the cultural fear of the dead rising from their graves to terrorize and afflict the community.
Scholars and archaeologists exploring these vampire burials are confronted with the challenge of deciphering the rationale behind these practices. Some theories suggest that these rituals were responses to disease outbreaks or catastrophic events, where communities sought supernatural explanations for inexplicable tragedies. Others propose that these measures were taken to pacify the fears of the living rather than to combat actual threats from the undead.
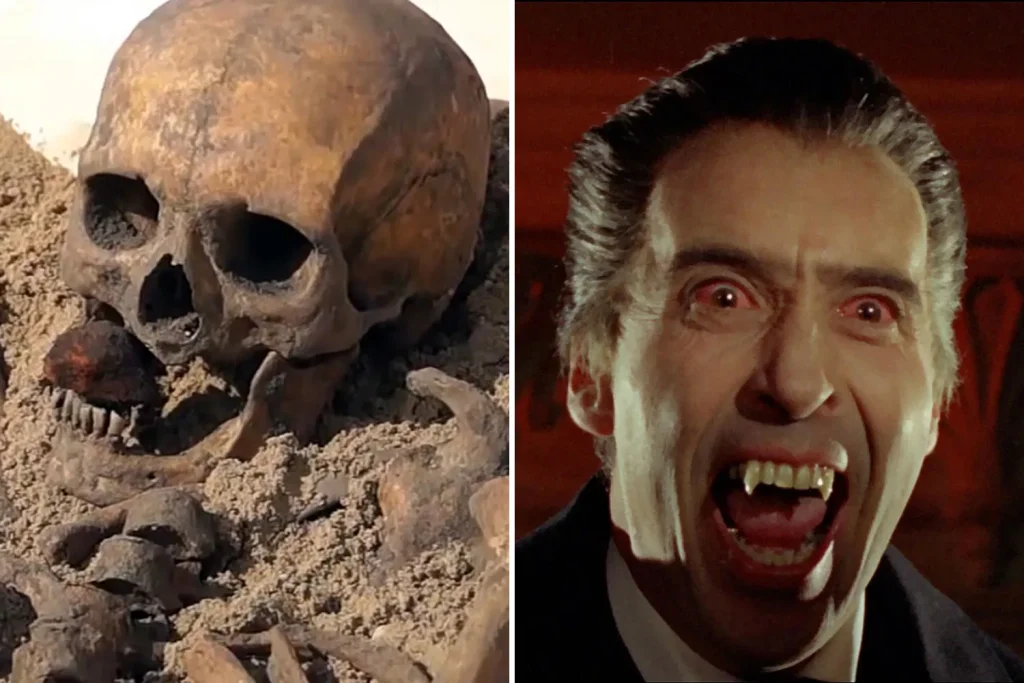

The significance of these discoveries extends beyond mere archaeological curiosities; they offer valuable insights into the belief systems and cultural perceptions of death and the supernatural in ancient societies. The practice of vampire burials highlights the enduring human fascination with the unknown and the lengths to which individuals and communities went to protect themselves from perceived threats, even after death.
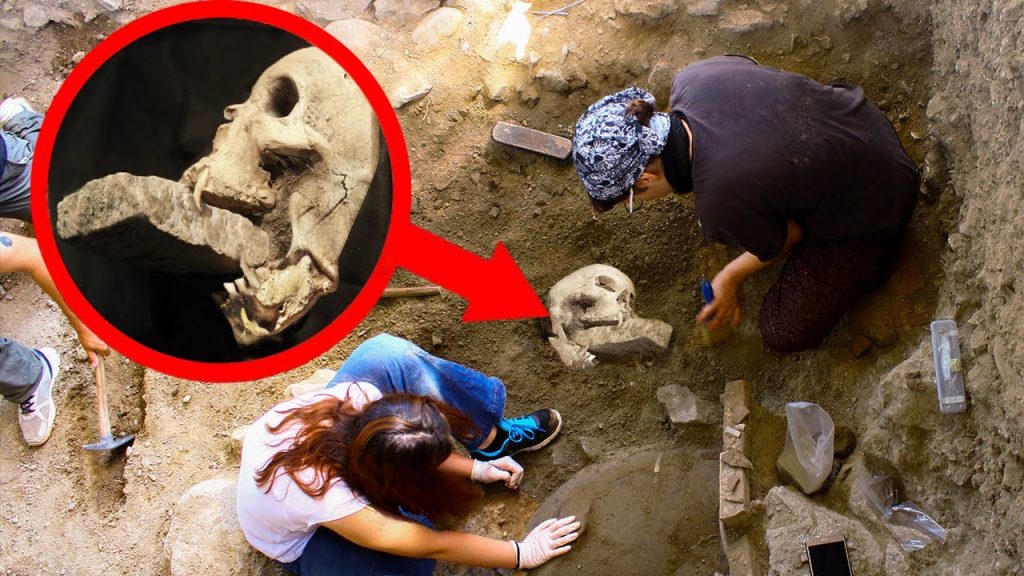

In conclusion, the enigmatic vampire burial rituals involving the insertion of stones into the mouth and the driving of stakes through the chest stand as captivating testaments to the complex beliefs and fears of ancient civilizations.
These practices, though eerie and perplexing to modern sensibilities, provide a glimpse into the profound influence of folklore, superstition, and the human quest for protection against the unknown forces of the supernatural.
The study of these rituals continues to unravel the mysteries of our ancestors’ beliefs and customs, inviting further exploration and scholarly inquiry into the rich tapestry of human history and culture.





