The death mask of Tutankhamun serves as a potent symbol of the youthful pharaoh’s divine status, royal lineage, and his passage into the realm of the afterlife. Below are several significant representations and symbolic interpretations attributed to Tutankhamun’s death mask:
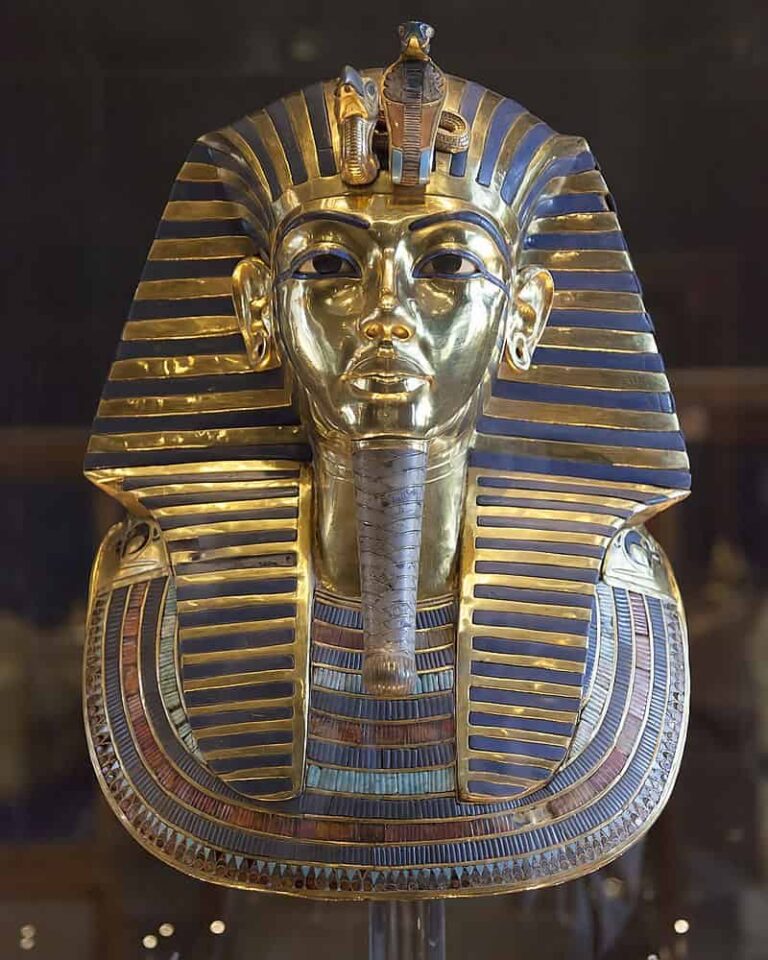

The death mask depicts Tutankhamun with idealized and youthful features, underscoring his divine stature. It presents the pharaoh as an everlasting and godly entity. Royal Insignia:
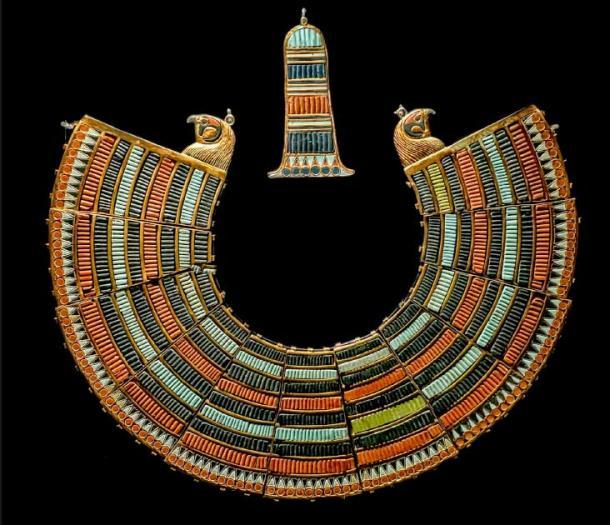
Adorned with emblems of royalty, such as the nemes headcloth adorned with a cobra (uraeus) and a vulture, the mask symbolizes the merging of Upper and Lower Egypt and the pharaoh’s dominion over the entire realm. Gold Significance:
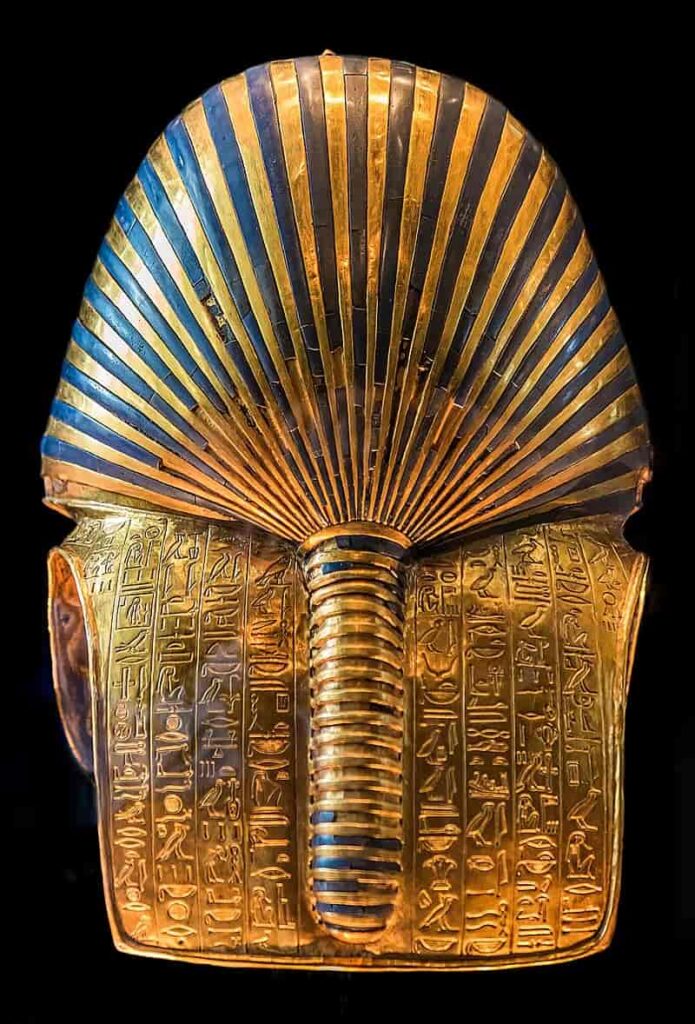

Fashioned from gold, the mask not only signifies opulence and extravagance but also highlights the pharaoh’s divine essence. In ancient Egyptian belief, gold was closely linked with the gods, and its inclusion in the mask accentuates Tutankhamun’s exalted spiritual standing. Protective Divinities:
The presence of the cobra and vulture atop the mask’s forehead symbolizes the goddesses Wadjet and Nekhbet, respectively. Wadjet, associated with safeguarding, was the guardian deity of Lower Egypt, while Nekhbet represented Upper Egypt. Together, they epitomize a unified and shielded realm. Spiritual Import:
Central to funerary rites, Tutankhamun’s death mask acted as a safeguarding shield for the pharaoh’s soul in the afterlife. Placed directly over the mummy’s visage within the tomb, it served a protective function. Eyes and Their Symbolism:
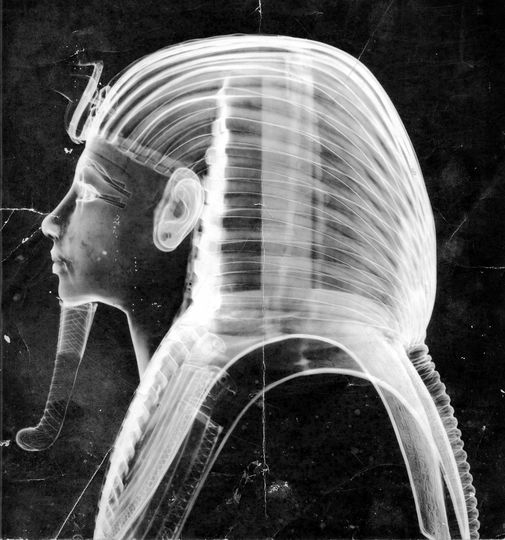
The eyes of the mask are adorned with inlays of obsidian and quartz, potentially symbolizing the sun and the moon. This dual representation could signify the cyclical pattern of existence, including life, death, and rebirth, as well as the perpetual voyage of the pharaoh through the realms of the afterlife.
With its ceremonial and ritualistic significance, the death mask played a pivotal role in the burial proceedings, underscoring the pharaoh’s divine transition to the hereafter. Its purpose was to guide Tutankhamun on his journey and ensure his protection and prosperity in the afterworld.





